Intelligent Doctor
Background
With the global pandemic of the New Coronavirus, ICU admission rates in hospitals around the world have skyrocketed. According to statistics, the rate of severe cases of New Coronavirus in the United States once reached 42%, putting great pressure on local medical resources and posing challenges to ICU clinicians, with the Daily Mail reporting several cases of patient deaths due to physician malpractice. With the excessive medical pressure, it is difficult to maintain a good condition for a long period of time with the ability of individual doctors alone.
We have tried to design AI-assisted software that can give clinical advice on the current patient’s clinical information to help clinicians quickly assess the patient’s condition and save time. Specifically, in the process of emergency treatment for critically ill patients, the AI will give the corresponding diagnosis text based on the current patient’s CT chest film and the anesthetic dose required for the emergency treatment surgery based on the patient’s current physiological indexes, which will reflect the patient’s current physiological condition to a certain extent and provide the clinician with the necessary diagnostic basis.
Technology
CT Inspection
The Vision Transformer-based CT intelligent diagnosis report combines computer vision and natural language processing algorithms, and the introduction of the memory driver module significantly improves the accuracy of the model when generating medium-length diagnosis reports.
Radiological reports are an important part of modern medical diagnosis. Radiology reports are an important component of modern medical diagnosis, where experienced physicians combine radiological images from various perspectives to provide a somatic report of the patient. With the Visual Transformer variant model, the AI can automatically generate reliable reports to assist physicians Diagnosis
Dose detection
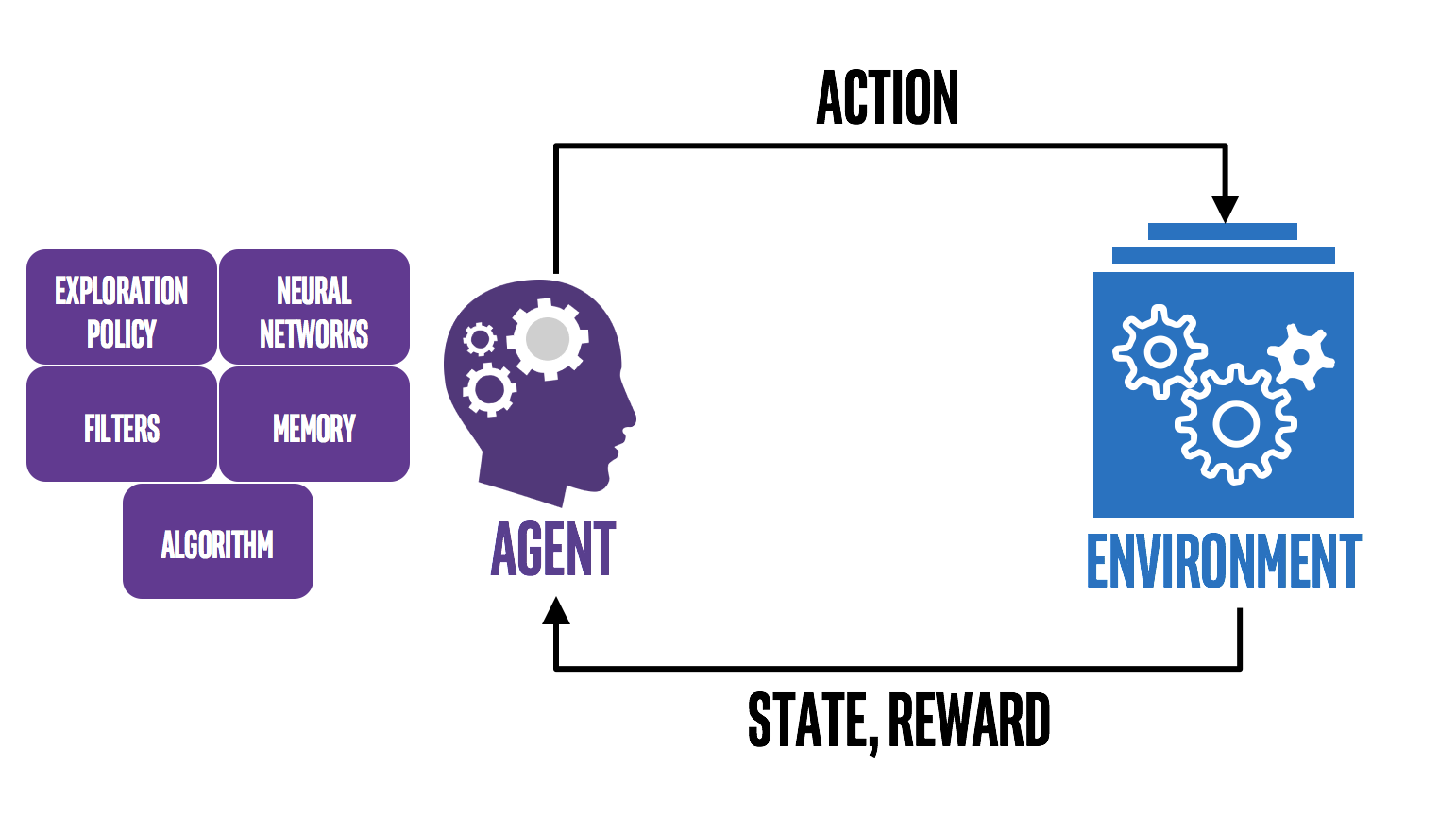
The offline deep reinforcement learning-based opioid dose recommendation technology also provides real-time clinically interpretable morphine dosing recommendations based on the changing pain and physiological conditions of different patients.
How much morphine to use for different patients is always a challenge that physicians have to face. In this activity, we want to use the morphine dose usage data provided in the MIMIC-IV dataset to personalize morphine dose usage recommendations for different patients with the help of a reinforcement learning approach. We broadly distinguish this module into two tasks: feature extraction and algorithm implementation.
state: The state is determined by the patient’s pain, the dose of adjunct analgesic used, the patient’s respiratory rate and the patient’s heart rate actions: We cut the continuous morphine dose into discrete 14 actions: 0, (0, 1], (1, 2], … , (20, inf)reward: The reward function takes into account heart rate, respiratory rate and the patient’s pain index. The reward is maximized when the pain is 0 and the respiratory rate and heart rate are in the acceptable range (between 60 and 100 for heart rate and between 12 and 20 for respiratory rate)
We use Q-Learning to make the model learn the optimal dose of sedation. Our model combines two extensions to the traditional deep Q network (DQN): the double-deep Q network (DDQ N), which avoids the problem of overestimation of value due to bootstrapping by separating action selection from value estimation, and the dual-deep Q network (dualing DQN), which improves the stability of the algorithm by bifurcating the The latter improves the stability of the algorithm by shunting the Q-value into two values: the state value and the action advantage. The model has two hidden layers, consisting of 64 and 256 nodes, respectively, with Leaky-ReLu activation functions and equally sized dominance and value streams.